Bacterial vaginosis
| Bacterial vaginosis | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
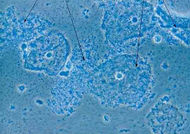 Micrograph of bacterial vaginosis - squamous cells of the cervix covered with rod-shaped bacteria, Gardnerella vaginalis (arrows). |
|
| ICD-10 | B96., N76. |
| ICD-9 | 616.1 |
| MeSH | D016585 |
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is the most common cause of vaginal infection. It is less commonly referred to as vaginal bacteriosis.[1] It is not considered to be a sexually transmitted infection.[2] BV is not transmitted through sexual intercourse but is more common in women who are sexually active.[3] BV is caused by an imbalance of naturally occurring bacterial flora and should not be confused with yeast infection (candidiasis), or infection with Trichomonas vaginalis (trichomoniasis), which are not caused by bacteria.
Contents |
Symptoms and signs
The most common symptom of BV is an abnormal homogeneous off-white vaginal discharge (especially after sex) with an unpleasant smell.[4] This malodorous discharge coats the walls of the vagina, and is usually without irritation, pain or erythema.
By contrast, menstrual blood does have a distinct odor[5]. Normal vaginal discharge will vary in consistency and amount throughout the menstrual cycle. A normal discharge is at its clearest about 2 weeks before the period starts.
Diagnosis
To make a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis, a speculum examination and subsequent swabs from high in the vagina should be obtained. These swabs should be tested for:
- A characteristic "fishy" odor on wet mount. This test, called the whiff test, is performed by adding a small amount of potassium hydroxide to a microscopic slide containing the vaginal discharge. A characteristic fishy odor is considered a positive whiff test and is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis.
- Loss of acidity. To control bacterial growth, the vagina is normally slightly acidic with a pH of 3.8–4.2. A swab of the discharge is put onto litmus paper to check its acidity. A pH greater than 4.5 is considered alkaline and is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis.
- The presence of clue cells on wet mount. Similar to the whiff test, the test for clue cells is performed by placing a drop of sodium chloride solution on a slide containing vaginal discharge. If present, clue cells can be visualized under a microscope. They are so-named because they give a clue to the reason behind the discharge. These are epithelial cells that are coated with bacteria.
Two positive results in addition to the discharge itself are enough to diagnose BV. If there is no discharge, then all three criteria are needed.[6] A 1990 study demonstrated that the single best test for BV was the test for clue cells on wet mount examination. The best combination of two tests for BV was the test for clue cells and the whiff test.[7]
Differential diagnosis for bacterial vaginosis includes the following:
- Normal discharge.
- Candidiasis (thrush, or a yeast infection).
- Trichomoniasis, an infection caused by Trichomonas vaginalis.
In clinical practice
In clinical practice BV is diagnosed using the Amsel criteria:[6]
- Thin, white, yellow, homogeneous discharge
- Clue cells on microscopy
- pH of vaginal fluid >4.5
- Release of a fishy odor on adding alkali—10% potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution.
At least three of the four criteria should be present for a confirmed diagnosis.[2]
An alternative is to use a Gram-stained vaginal smear, with the Hay/Ison[8] criteria or the Nugent[9] criteria. The Hay/Ison criteria are defined as follows:[2]
- Grade 1 (Normal): Lactobacillus morphotypes predominate.
- Grade 2 (Intermediate): Mixed flora with some Lactobacilli present, but Gardnerella or Mobiluncus morphotypes also present.
- Grade 3 (Bacterial Vaginosis): Predominantly Gardnerella and/or Mobiluncus morphotypes. Few or absent Lactobacilli. (Hay et al., 1994)
What this technique loses in interobserver reliability, it makes up in ease and speed of use.
The standards for research are the Nugent[9] Criteria. In this scale, a score of 0-10 is generated from combining three other scores. This method is time consuming and requires trained staff, but it has high interobserver reliability. The scores are as follows:
- 0–3 is considered negative for BV
- 4–6 is considered intermediate
- 7+ is considered indicative of BV.
At least 10–20 high power (1000× oil immersion) fields are counted and an average determined.
|
Lactobacillus morphotypes — average per high powered (1000× oil immersion) field. View multiple fields. |
Gardnerella / Bacteroides morphotypes — average per high powered (1000× oil immersion) field. View multiple fields. |
Curved Gram variable rods — average per high powered (1000× oil immersion) field. View multiple fields (note that this factor is less important — scores of only 0–2 are possible) |
|
|
|
A recent study [10] compared the gram stain using the Nugent criteria and the DNA hybridization test Affirm VPIII in diagnosing BV. The Affirm VPIII test detected Gardnerella in 107 (93.0%) of 115 vaginal specimens positive for BV diagnosed by gram stain. The Affirm VPIII test has a sensitivity of 87.7% and specificity of 96% and may be used for the rapid diagnosis of BV in symptomatic women.
Causes
A healthy vagina normally contains many microorganisms; some of the common ones are Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus jensenii. Lactobacillus, particularly hydrogen peroxide-producing species, appears to help prevent other vaginal microorganisms from multiplying to a level where they cause symptoms. The microorganisms involved in BV are very diverse, but include Gardnerella vaginalis, Mobiluncus, Bacteroides, and Mycoplasma. A change in normal bacterial flora including the reduction of lactobacillus, which may be due to the use of antibiotics or pH imbalance, allows more resistant bacteria to gain a foothold and multiply. In turn these produce toxins which affect the body's natural defenses and make re-colonization of healthy bacteria more difficult.
There are a variety of causes for bacterial vaginosis. Cases of bacterial vaginosis are more likely to occur in sexually active women between the ages of 15 and 44, especially after contact with a new partner. Condoms may provide some protection and there is no evidence that spermicide increases BV risk. Although BV can be associated with sexual activity, there is no clear evidence of sexual transmission.[11] It is possible for virgins to get infected with bacterial vaginosis. Rather, BV is a disordering of the chemical and biological balance of the normal flora. Recent research is exploring the link between sexual partner treatment and eradication of recurrent cases of BV. Pregnant women and women with sexually transmitted infections are especially at risk for getting this infection. Bacterial vaginosis may sometimes affect women after menopause. A 2005 study by researchers at Ghent University in Belgium showed that subclinical iron deficiency (anemia) was a strong predictor of bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women [12]. A longitudinal study published in February 2006 in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology showed a link between psychosocial stress and bacterial vaginosis independent of other risk factors[13].
Complications
Although previously considered a mere nuisance infection, untreated bacterial vaginosis may cause serious complications, such as increased susceptibility to sexually transmitted infections including HIV, and may present other complications for pregnant women.[14]
Treatment
Antibiotics
Metronidazole or clindamycin either orally or vaginally are effective treatment.[15] However, there is a high rate of recurrence.[11]
The usual medical regimen for treatment is the antibiotic Metronidazole (500 mg twice a day, once every 12 hours) for 7 days.[16] A one-time 2g dose is no longer recommended by the CDC because of low efficacy. Extended release metronidazole is an alternative recommendation.
In contrast to some other infectious diseases affecting the female genitals, according to some sources, treatment of the sexual partners is not necessarily recommended.[17]
Alternative medicine
In 2009 one Cochrane review did not find probiotics useful in the treatment of BV[18] while another concluded they were effective when combined with antibiotics.[15]
Epidemiology
It is estimated that 1 in 3 women will develop the condition at some point in their lives.[19]
See also
- Non-specific urethritis
References
- ↑ "Vaginal Infections -- How to Diagnose and Treat Them: Bacterial Vaginosis or Vaginal Bacteriosis". Medscape. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/463842_3. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "National guideline for the management of bacterial vaginosis (2006)". Clinical Effectieness Group, British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH). http://www.guideline.gov/summary/summary.aspx?doc_id=11602.
- ↑ "Vaginal infections". http://women.webmd.com/guide/sexual-health-vaginal-infections?page=2.
- ↑ http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm070969.pdf
- ↑ http://wguide.uchicago.edu/3sexed.html
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Amsel R, Totten PA, Spiegel CA, Chen KC, Eschenbach D, Holmes KK (1983). "Nonspecific vaginitis. Diagnostic criteria and microbial and epidemiologic associations". Am. J. Med. 74 (1): 14–22. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(83)91112-9. PMID 6600371.
- ↑ Thomason JL, Gelbart SM, Anderson RJ, Walt AK, Osypowski PJ, Broekhuizen FF (1990). "Statistical evaluation of diagnostic criteria for bacterial vaginosis". Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 162 (1): 155–60. PMID 1689107.
- ↑ Ison, CA; Hay, PE (2002). "Validation of a simplified grading of Gram stained vaginal smears for use in genitourinary medicine clinics". Sex Transm Infect 78 (6): 413–5. doi:10.1136/sti.78.6.413. PMID 12473800.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Nugent RP, Krohn MA, Hillier SL (1991). "Reliability of diagnosing bacterial vaginosis is improved by a standardized method of gram stain interpretation". J. Clin. Microbiol. 29 (2): 297–301. PMID 1706728. PMC 269757. http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1706728.
- ↑ Gazi H, Degerli K, Kurt O, et al. (2006). "Use of DNA hybridization test for diagnosing bacterial vaginosis in women with symptoms suggestive of infection". APMIS 114 (11): 784–7. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2006.apm_485.x. PMID 17078859.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Bradshaw CS, Morton AN, Hocking J, et al. (2006). "High recurrence rates of bacterial vaginosis over the course of 12 months after oral metronidazole therapy and factors associated with recurrence". J. Infect. Dis. 193 (11): 1478–86. doi:10.1086/503780. PMID 16652274.
- ↑ Verstraelen, H; Delanghe, J; Roelens, K; Blot,S; Clauys, G and Temmermann, M (2005): Subclinical iron deficiency is a strong predictor of bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy.BMC Infect Dis. 2005; 5: 55.
- ↑ Nansel,TR; Riggs, MA; YU, KF and Andrews, WW: The association of psykhosocial stress and bacterial vaginosis in a longitudinal cohort Am.J Obst. Gynecol. 194, (2), p 381-386
- ↑ "STD Facts - Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)". CDC. http://www.cdc.gov/std/bv/STDFact-Bacterial-Vaginosis.htm#Complications. Retrieved 2007-12-04.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Oduyebo OO, Anorlu RI, Ogunsola FT (2009). "The effects of antimicrobial therapy on bacterial vaginosis in non-pregnant women". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD006055. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006055.pub2. PMID 19588379.
- ↑ http://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/2006/vaginal-discharge.htm
- ↑ Potter J (November 1999). "Should sexual partners of women with bacterial vaginosis receive treatment?". Br J Gen Pract 49 (448): 913–8. PMID 10818662. PMC 1313567. http://openurl.ingenta.com/content/nlm?genre=article&issn=0960-1643&volume=49&issue=448&spage=913&aulast=Potter.
- ↑ Senok AC, Verstraelen H, Temmerman M, Botta GA (2009). "Probiotics for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD006289. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006289.pub2. PMID 19821358.
- ↑ "The Family Planning Association". http://www.fpa.org.uk.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||